 The European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) regularly conducts studies to see how piracy rates evolve over time.
The European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) regularly conducts studies to see how piracy rates evolve over time.
These studies also help the public and lawmakers identify the various barriers and drivers behind this activity. That can help to shape future policies.
This week, the EU Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) published the latest version of its triannual Intellectual Property and Youth Scoreboard 2022. The research draws on a survey of 22,021 young people (aged 15 to 24) across all EU Member States conducted earlier this year.
The latest report is the third installment which makes it possible to track how the piracy habits of EU youth developed over time. One of the main conclusions identifies a gradual decline in the percentage of people that pirated at least once in the past year.
33% Pirates
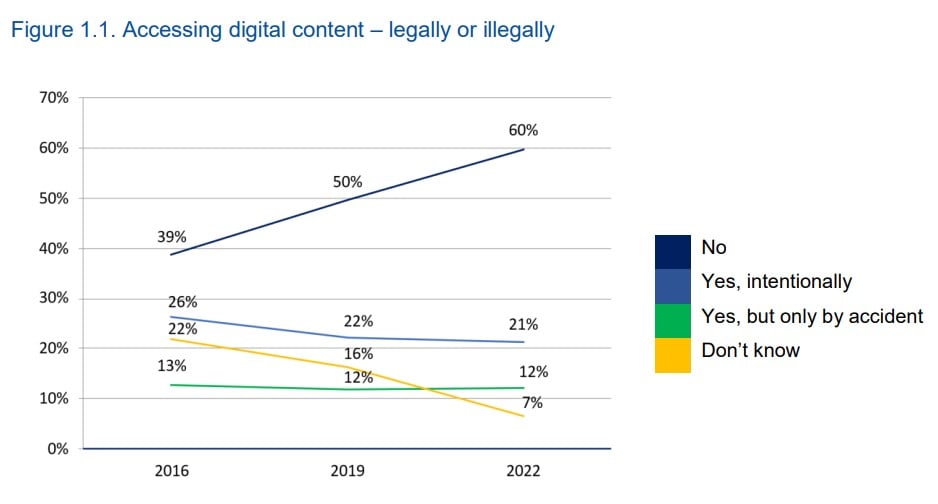
The piracy rate in the EU dropped from 39% in 2016 to 33% this year. While many young people admit that they pirated something over the past twelve months, roughly a third of this group did so "by accident." That leaves us with 21% who are intentionally pirating. Meanwhile, the majority of EU youth (60%) haven't pirated a single thing.
There are some significant differences in piracy rates between countries. In Malta, for example, more than 50% of the youth admitted to accessing content illegally, while only 25% in Germany did so.
It is worth emphasizing that only a tiny fraction of the population exclusively consumes pirated content. Most use a mixture of legal and illegal sources. Again, there are massive differences between countries. In France, nearly 10% of the consumers pirate music exclusively but in the Netherlands the figure is just 1.5%.
Well Edudated Intentional Pirates
One particularly interesting finding is that piracy rates are significantly higher among well-educated youth. Of those who have a university degree, 28% have intentionally pirated something over the past year. That's nearly twice as much as those who have no or some secondary education (15%).
EU youth with secondary to college education end up in the middle, with 21% admitting to intentionally pirating content. That's the same percentage as the EU average across all youth.

While cost is often mentioned as a reason to use pirate sites and services, students with an income pirated more often (24%) than those who don't have a job (18%). Perhaps the first group values their hard-earned money more, while the latter is sponsored by their parents.
Reasons to Pirate
Availability and affordability continue to be the prime reasons why many people use pirate sites and services. More than half (55%) mentioned cost as the primary factor, followed by a lack of availability, which 25% cited as the main reason.
Interestingly, too much 'availability' can become a problem as well. With content spread out over several subscription services, enjoying movies and TV shows legally has become quite costly. The EU report also picked up on this.
"[W]hile there were now more legal sources, this diversification meant that content was increasingly spread over multiple sources, forcing consumers to take out more subscriptions if they wanted to maintain access to a range of content," the report reads.
Related to this, some people turned to piracy because a TV show they could previously watch legally was suddenly pulled from the platform. One respondent cited in the report described the following experience.
"I was watching a series on Netflix and then they took it down from Netflix. Because I still wanted to finish the series I continued to search the internet and ended up on an illegal site."

Reasons to Stop
Copyright holders will mostly be interested in what would make people think twice about downloading or streaming content from pirate sites. In response to this question, most people (53%) mentioned the risk of running into viruses and malware as the main reason.
Other potential reasons include credit card theft (49%), the risk of getting caught and punished (36%), or the fact that creators and legal services could be hurt financially (26%).
The suggestion that the money made by pirate sites and services could go to organized crime wasn't very popular. In fact, many people have a hard time believing that this is actually true.
"Participants had generally not previously considered that there might be a link between organized crime and illegal sources of content. Indeed, when this topic was raised in the communities, there was significant scepticism as to whether such a link existed."
All in all, the EUIPO report provides some great insights. While piracy continues to decline among the youth, it remains a significant problem. And new trends such as the increase in subscription services, may actually breed a new generation of pirates.
From: TF, for the latest news on copyright battles, piracy and more.
No comments:
Post a Comment