 Twenty years ago, a new trend called file-sharing started to conquer the Internet.
Twenty years ago, a new trend called file-sharing started to conquer the Internet.
What used to be a niche activity, only reserved for the technically inclined, suddenly became a popular pastime for the masses.
At the turn of the century, Napster was the first to be widely embraced, which happened to be right around the time MP3 players became popularized as well.
This new sharing culture did not just intrigue music-loving teens. It offered limitless inspiration for many developers as well. In the year following Napster's release, other P2P applications such as Direct Connect, iMesh, eDonkey2000, Freenet, and LimeWire launched.
Napster initially remained the most popular application but this reign ended in the summer of 2001, when it was ordered to shut down by a US federal court. By then, however, its successors were queuing up to take over, and LimeWire stood out.
LimeWire's 'Slow' Start in 2000
LimeWire was founded by entrepreneur and hedge fund manager Mark Gorton. The application was created under the wings of Lime Group, LLC, by a small group of developers with a keen interest in peer-to-peer technology.
According to the online history books, the Gnutella-based software was first released on May 3, 2000. However, at the time, it wasn't called LimeWire yet. The application as people know it, the Gnutella-based file-sharing client, came out a few months later.
"To say we had a slow start was an understatement. At the time, we celebrated every 100 downloads and then every thousand but that was just a drop in the bucket," Greg Bildson, former LimeWire CTO/COO, and employee of the first hour, recalls.
"Newer clients like LimeWire were definitely an improvement on the Gnutella network but we were still only a tiny fraction of the network," he adds.
Limewire Interface
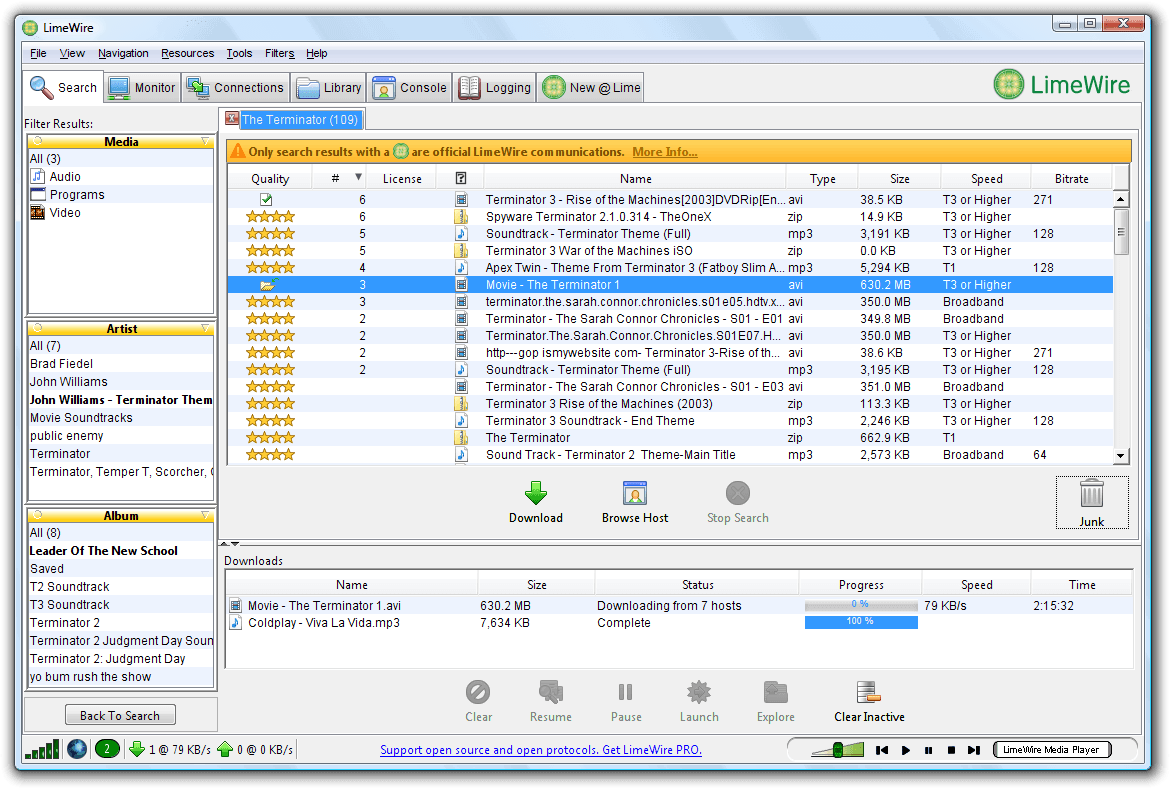
That slow start should be seen in perspective. While the official Gnutella client from Nullsoft was much more popular early on, LimeWire caught up quickly. Within a year more than three million copies of the software were downloaded, something most developers could only dream of.
LimeWire's Explosive Growth
During the time the file-sharing business was booming, LimeWire grew faster than other applications. This growth was helped by the shutdown of competitors such as Napster and Grokster. Also, the site was less aggressive on ads and toolbars than some competitors.
This doesn't mean that it didn't have downsides of course. The Gnutella network was dealing with spam and fakes, for example, where the files were not always what they promised to be.
Many former users will be familiar with the frustration of downloading a music track, to realize after half an hour of downloading it wasn't what its title promised. At the time, that was all part of the game.
Despite the drawbacks, LimeWire became the dominant file-sharing tool during the first decade of this millennium. While BitTorrent generated more traffic, LimeWire appealed to a broader audience of casual file-sharers.
One in Five PCs had LimeWire
Around its height in the mid-2000s, roughly one in five of all PCs in the world had a copy of the software installed.
The software became the go-to tool for millions of people, many of whom used it to fill up their MP3 players. At the same time, heaps of money were flowing in thanks to people who paid for the 'Pro' version, even though a pirated copy could be downloaded with the free LimeWire version.
Limewire Pro

With LimeWire's first release now twenty years ago and its eventual demise ten years later, we decided to reach out to some people who were working for the company at the time. We spoke to Angel Leon, Zlatin Balevsky, and Dave Nicponski, three members of the LimeWire team.
LimeWire Developers Look Back
Over the years many stories have been told about LimeWire but we wanted to hear from insiders why they think their software became such a success.
Leon, who later started the LimeWire spinoff FrostWire, joined in 2005 after responding to a Craigslist ad. He became the webmaster for Limewire.com and Magnetlink.com but, along the way, mastered the application's code as well.
According to Leon, the LimeWire developer team was very talented and the technology itself worked well. However, the success, as is often the case, also came down to timing.
"The technology was very easy to use, search, download, share all in one place. The project was developed and maintained by a group of very talented developers, truly a world-class team," Leon says.
"But I think they rode greatly on the circumstances, soon after I got there, if I remember correctly there was a ruling against Grokster, I imagine they took in a lot of their userbase," he adds.
Nicponski joined the LimeWire team in 2004 but already was an experienced P2P developer by then, as he worked at Bearshare since 2001. There was a healthy competition between the two teams as both were trying to build the best and most appealing file-sharing application.
Why LimeWire eventually became the most popular of the two is still a mystery to him and there probably was a bit of luck involved
"In many ways, BearShare was a technically superior product, but at the end of the day, that wasn't the primary differentiating factor which determined popularity. I don't rightly know what was. I suspect a combination of branding and a whole lot of luck," Nicponski says.
Balevsky also joined the LimeWire team in early 2004, while he was still at university. He reached out to the company directly to see if LimeWire was hiring, while offering a solution to a problem they were trying to solve.
"I was contributing to an open-source project called Freenet which was written in Java and saw that LimeWire was trying to solve a problem I had already solved," Balevsky tells us.
This initial offer was rejected but after some time had passed, Greg Bildson invited him for a job interview, after which he joined the team as a developer.
Spyware Free
According to Balevsky, the team worked very hard to create the ultimate file-sharing experience. However, he believes that LimeWire's success also stems from the fact that it was relatively clean, while other software was bundled with adware and toolbars.
"That wasn't always the case – when I first joined we did bundle some third-party software in the 'basic' version. I remember clearly that within a month or so of removing the adware our popularity had exploded," Balevsky says.
LimeWire was also relatively virus-free in the early years. This set it apart from competitors such as Kazaa, whose hashing algorithm allowed viruses and fake files to masquerade as genuine.
"The virus writers eventually figured out how to use LimeWire as an infection vector, but that didn't happen until years later which gave us plenty of time for good publicity," Balevsky notes.
Limewire.com in 2004: Faster Than Kazaa, No Spyware
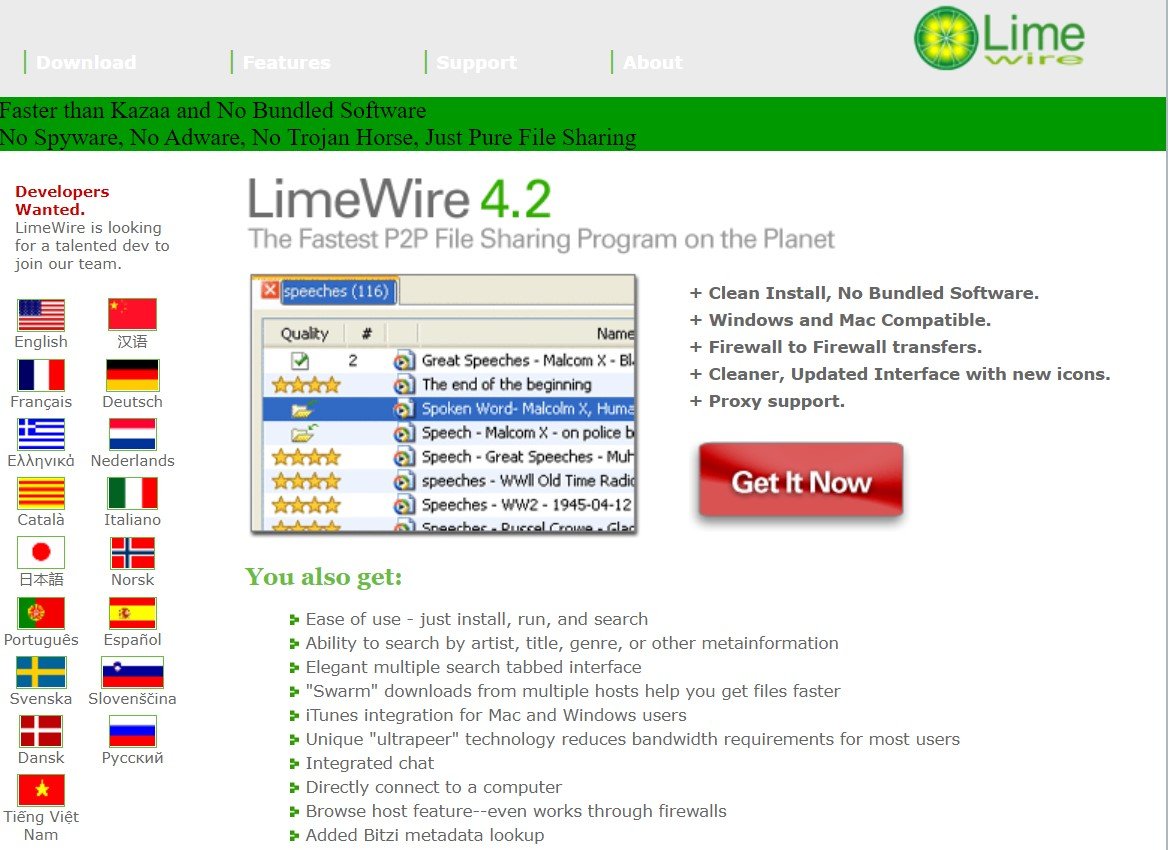
In the meantime, life was good at the LimeWire office. There was an open-source mentality and the company itself was very open as well, involving and respecting all team members. The was no shortage of money either and the sky was the limit.
Rooftop Parties and a $300 Waterpipe
Leon recalls LimeWire's well-known rooftop parties which attracted many outsiders as well, including Casey Neistat and his brother. Located in Manhattan, the Limewire building had a great location with a terrace of top and a view of the New York skyline.
Limewire's rooftop terrace
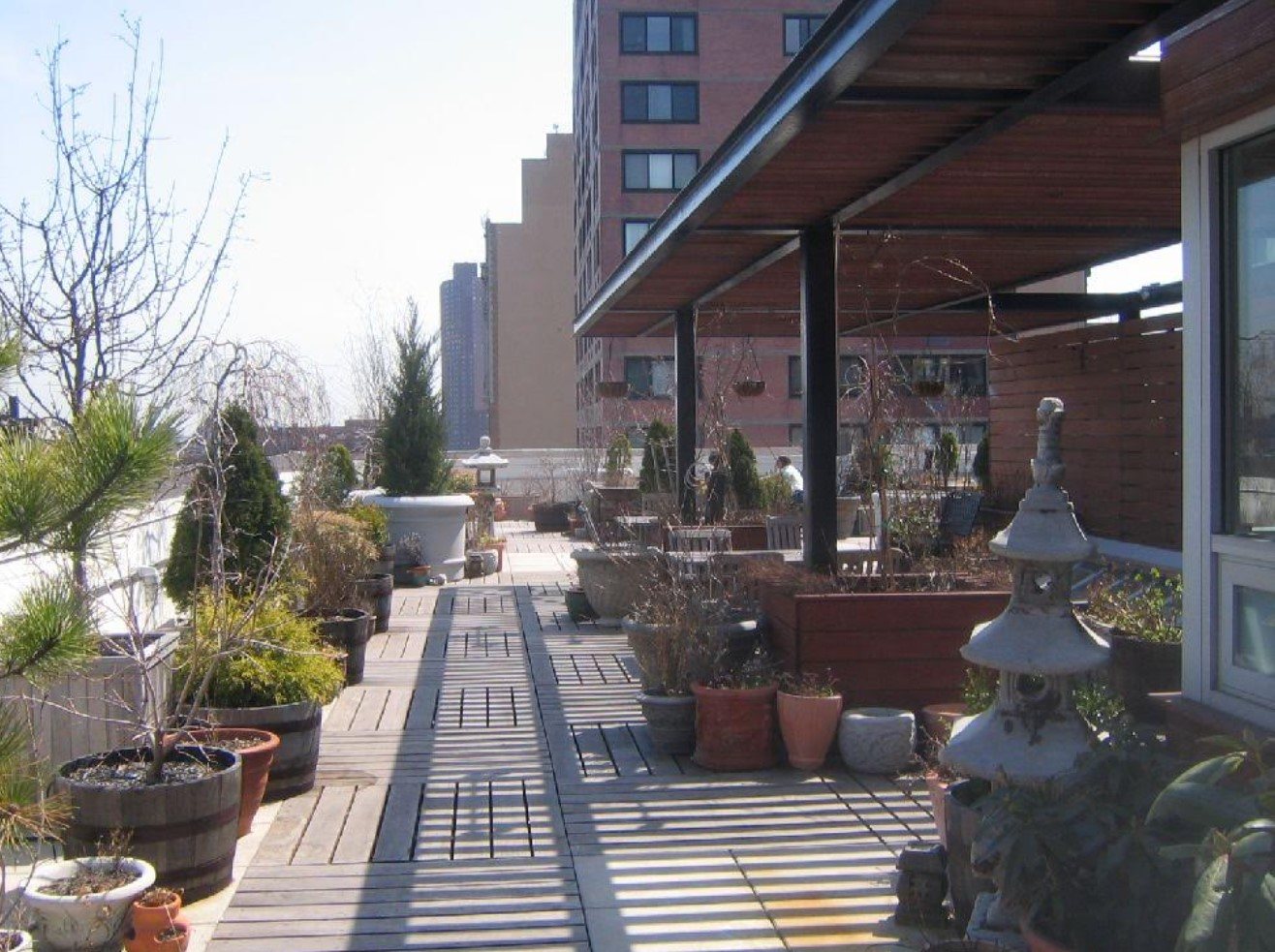

This team of young and talented people worked hard but also knew how to enjoy life. Balevsky seconds this party atmosphere, as well as the company's openness.
"We were young, crazy, had virtually no management or oversight as the bosses let us do whatever we wanted," he says, adding that he is reluctant to share too much as that may make some former colleagues uncomfortable.
"The fact that we had a $300 fancy waterpipe in the office – a gift from the owner – should give you enough of an idea of what the atmosphere and culture were like."
"The inventor of Kademlia – Petar Maymunkov worked in a different company owned by the same owner so we had many in-depth technical discussions over a waterpipe and poker."
Lawsuit Shuts LimeWire Down
LimeWire's seemingly limitless expansion eventually came to an end. This started in 2006 when a group of music companies, represented by the RIAA, sued Lime Group over copyright infringement. Leon had left the company by then but was served nonetheless.
"I was still served with a subpoena with very loud and scary bangs at my Bushwick, Brooklyn apartment one early morning. LimeWire was kind enough to take care of my legal bills at the time," he recalls.
Nicponski was more directly involved in the lawsuit and he was deposed for roughly eight hours by New York lawyers working for the major music labels.
"It was a bit surreal to have to give testimony to a small army of lawyers at the top of a Manhattan skyscraper for an early-twenty-something," Nicponski says, while highlighting another important point.
Looking back, many people believe that the file-sharing boom helped to change the music industry. While the labels witnessed a loss of control and income, people including Nicponski see things differently.
"My general feelings during that deposition were that I had helped open the pandora's box of technology against an industry that I viewed (and still view) as overwhelmingly evil. We exposed the cracks in the foundation of that business, and once the cracks started to appear, they then began to widen."
In a way, file-sharing helped to break up the music industry monopoly, turning music into a community. This meant more choice for consumers and paved the way for "per song" sales, new distribution models such as Apple's iTunes, and eventually streaming.
The LimeWire lawsuit was expected to a degree and didn't come as a shock. However, as the legal battle dragged on for several years, uncertainty grew at the LimeWire office. While Mark Gorton explored several options to survive, the end was always near.
"Every other Friday was the last day at work, we had at least three 'Goodbye dinners' and in general development stagnated due to the uncertainty," says Balevsky, who was still with the team.
Balevsky, in the meantime, started to help Leon and another developer with the FrostWire spinoff. This would ensure that the LimeWire spirit would survive, even after the company shut down.
LimeWire's demise eventually came in 2010. Facing trillions of dollars in potential damages, Lime Group LLC decided to settle the lawsuit. The company agreed to pay $105 million in damages and a message on the official site urged users to remove the software.
The end of an era
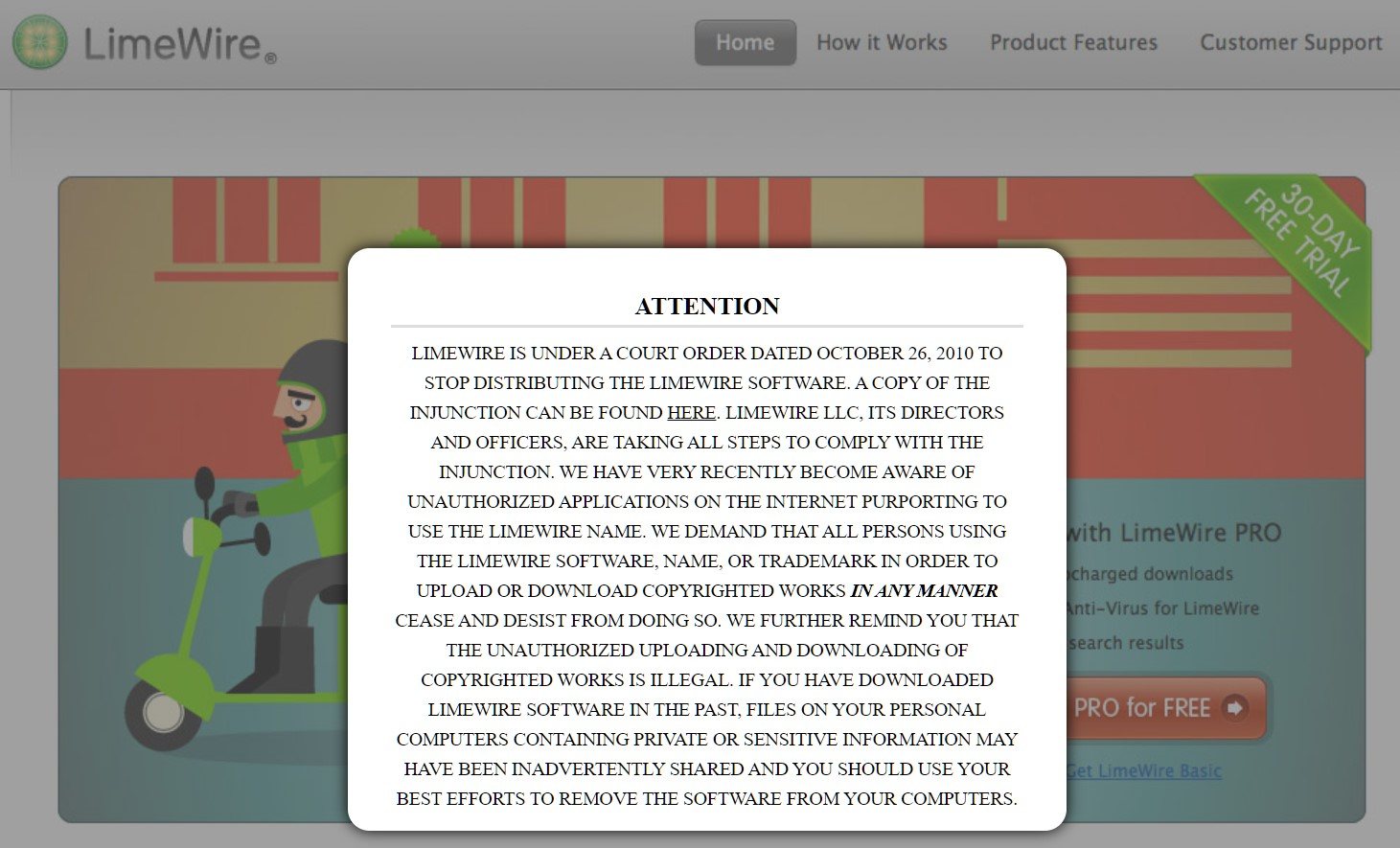
People who visit LimeWire.com today will no longer see the shutdown notice. The domain was eventually taken over by Balevsky who uses it to promote his own anonymous file-sharing application MuWire.
The developer never witnessed LimeWire's end as he left the company in 2008 after obtaining his green card. Leon was gone by then too, and continued working on FrostWire, which despite troubles with Google's Play store, is still around today.
With LimeWire gone, the name lives on in the memories of millions of people, and partially in FrostWire and MuWire. What happened to the $300 waterpipe is unclear, however.
From: TF, for the latest news on copyright battles, piracy and more.
No comments:
Post a Comment